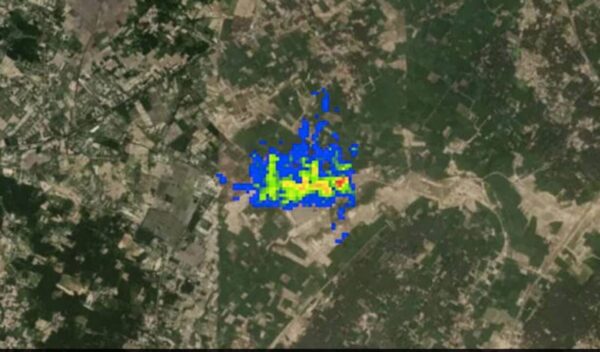
A high-decision satellite tv for pc photograph taken much less than forty eight hours in the past suggests a cloud of the effective greenhouse fueloline methane close to a waste facility in India. The photograph is the second one in a chain of unique observations Bloomberg Green will submit at some stage in COP27 from emissions tracking corporation GHGSat Inc.
The detection highlights how piles of garbage – which generate the amazing greenhouse fueloline while natural fabric like meals scraps damage down withinside the absence of oxygen – are triggering a number of the global’s most powerful and maximum continual methane emissions.
Landfills and wastewater are liable for approximately 20% of the methane emissions generated from human activity.
The satellite tv for pc photograph became taken at 1:28 pm Mumbai time on Nov. five and suggests a plume of methane that GHGSat attributed to a landfill in India. The expected emissions charge became 1,328 kilograms consistent with hour of methane. Landfills have a tendency to be continual emitters, in keeping with the Montreal-primarily based totally company.
Scientists say decreasing the emissions of the amazing greenhouse fueloline, which has eighty four instances the warming strength of carbon dioxide at some stage in its first a long time withinside the surroundings, is one of the quickest and most inexpensive methods to chill the planet.
Failing to minimize releases from the waste region should derail worldwide weather goals. Diverting meals scraps and different organics earlier than they input a landfill is important to proscribing destiny emissions. The effect of legacy dumps may be mitigated via aerating piles of trash and fueloline seize systems.
The modern imagery comes as global leaders acquire in Egypt this week to talk about weather alternate policy, with the UN caution that worldwide temperatures in 2022 are in all likelihood to stop approximately 1.15C above the common in pre-business instances, making it the 5th or 6th freshest yr on record.
China
The first photograph withinside the series, posted Sunday, confirmed six methane releases in northeast China close to the Daqing oilfield, in keeping with GHGSat. Estimated emissions charges ranged among 446 and 884 kilograms consistent with hour and the cumulative charge became 4,477 kilograms an hour.
If the releases lasted for an hour at that charge they might have the equal short-time period weather effect because the annual emissions from approximately eighty one US cars.
Methane is the number one issue of herbal fueloline and liable for approximately 30% of the Earth’s warming.
Leaks can arise at some stage in extraction and shipping of the fossil fuel, however methane is likewise robotically generated as a byproduct of oil and coal manufacturing and if operators do not have infrastructure to get the fueloline to marketplace they’ll launch it into the surroundings. The International Energy Agency has referred to as for oil and fueloline operators to halt all non-emergency methane venting.
The detections spotlight the unexpectedly increasing cappotential of satellites to perceive and tune methane nearly everywhere withinside the global this is using a brand new generation of weather transparency wherein greenhouse gases may be quantified and attributed in close to real-time to man or woman belongings and businesses.
More businesses and establishments are launching multi-spectral satellites which could discover methane’s precise signature. GHGSat has six satellites in orbit now devoted to tracking business methane and ambitions to release some other 5 through the stop of subsequent yr.
US non-income Environmental Defense Fund plans to release its MethaneSAT in 2023 and a consortium along with Carbon Mapper, the country of California, NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory and Planet Labs expects to release satellites subsequent yr.
In 2021, concentrations of methane withinside the surroundings had the most important yr-on-yr soar considering measurements started out 4 a long time in the past, in keeping with the World Meteorological Organization.